Tongue tie is a common ailment for many people, but it can be treated if you know the right information about it. There are a variety of treatments available, and you should learn about the causes, symptoms, and options before you decide on the treatment plan that best suits your needs.
Treatment options
If your child suffers from tongue tie in Noida, there are treatment options available to improve his or her condition. Some treatments are non-surgical, while others are surgical. In either case, it is important to consult with a professional dentist.
Tongue-tie is an oral disorder that affects babies and kids of all ages. It can interfere with their feeding and speech. As a result, they may be at risk for malnutrition or poor weight gain.
To properly diagnose a tongue tie, a child’s health history and physical examination will be required. A dentist in Noida can also perform a thorough exam and discuss treatment options with you.
One of the most common causes of tongue tie is a defect in the frenulum, which is a small band of tissue located at the bottom of the mouth. This tissue is meant to connect the tongue to the floor of the mouth. However, if the frenulum is too short, or too thick, it can cause problems with feeding and speaking.
The most effective treatment for a tongue tie is to have the lingual frenulum relax, allowing the tongue to move more freely. Surgical techniques, such as a frenectomy, frenuloplasty, or frenotomy, may be used to correct the problem.
A more complex surgical procedure, known as frenuloplasty, involves reshaping the frenulum. These types of surgeries are generally performed on infants and children, but adults can benefit from the procedure as well.
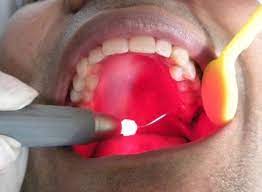
During the surgery, a doctor will reshape the frenulum by using sutures to prevent the knot from reforming. They can also use lasers to seal blood vessels and lymphatic vessels, resulting in minimal bleeding and faster healing.
There are several risks involved in tongue tie surgery, including injury to saliva ducts and delayed healing. Depending on your child’s age and the type of tongue tie, he or she may need to undergo speech therapy as part of the recovery process.
Symptoms
The tongue is connected to the mouth by a thin piece of skin called the frenulum. A tongue tie is when the frenulum is short, limiting the tongue’s range of motion.
To be diagnosed, a child’s doctor will perform a physical exam and may use an assessment tool to check for a tongue tie. In some cases, the baby will be referred to an ENT for formal diagnosis.
Treatment of a tongue tie can vary depending on the patient’s age, severity, and other factors. It’s important to take the proper steps to ensure your child is receiving the best care possible.
Tongue tie is a congenital condition that occurs in 4-11% of newborns. This condition can cause trouble with breastfeeding, which can lead to malnutrition. If your infant’s condition is more severe, he or she may need surgery.
Some babies can go without any treatment for a while. During this time, a healthcare provider may recommend the use of a device called a frenotomy. Usually, the procedure is performed with sterile scissors or a laser. After the frenotomy, the baby should be able to feed.
A more complex tongue tie procedure, called a frenuloplasty, is used in more severe cases. It is typically done under general anesthesia.
Tongue tie can affect any gender, but is most common in boys. Males are three times more likely to develop the condition than girls.
The most common symptom of a tongue tie is the limited movement of the tongue. This can make brushing teeth and other oral activities challenging. Another symptom is a gap between the lower front teeth.
Other symptoms can include a poor latch, cracked nipples, and pain after feeding. If these symptoms persist, the parent should consider a visit to an ENT or lactation consultant.
Causes
Tongue tie is a disorder where there is a gap or short strip of tissue that connects the tip of the tongue to the lower gum. This can cause problems with chewing, swallowing, and oral hygiene. It can also affect the development of your child’s speech.
There are two common types of tongue-tie. The first is an anterior tongue-tie, which is easy to spot during a physical exam.
The second type of tongue tie is a posterior tongue-tie, which is harder to diagnose. During a physical examination, your doctor will check your baby’s tongue. If there is a gap, the lingual frenulum will be visible.
In severe cases, your healthcare provider may recommend surgery. A frenectomy, also called a frenotomy, involves cutting the lingual frenulum, which allows the tongue to be released.
Your baby should be able to recover quickly from a frenotomy. You may need to give your baby an anaesthetic to ensure that the procedure goes smoothly.
Some children who have tongue-ties have trouble eating or speaking. If this is the case, your child will need to be examined by an otolaryngologist. They can then make a diagnosis and recommend a treatment plan.
Some babies with tongue-ties may have difficulty latching on to breasts or bottles. This can lead to malnutrition. Also, the child’s airway may become smaller, which can prevent the child from breathing normally.
Tongue-ties can also interfere with your child’s ability to brush his or her teeth. Depending on the condition, you may need to have your baby’s mouth checked more often. Symptoms can include a gap between the bottom front teeth.
Tongue-ties are generally mild, and your doctor may not need to correct them. However, if your child is experiencing significant symptoms, your healthcare provider may need to perform a surgical procedure to remove the tongue-tie.
Treatment for ankyloglossia
If your baby has been diagnosed with ankyloglossia (tongue-tie), you may be wondering what treatment options are available. Tongue-tie is a congenital anomaly of the tongue, which occurs when the lingual frenulum is abnormally short. This lack of mobility can hinder speech, swallowing, and chewing.
A tongue-tie is often discovered in babies when they are unable to breastfeed. However, ankyloglossia also affects older children. Although the exact causes of ankyloglossia are unknown, it appears to be hereditary.
Treatment for ankyloglossia involves surgical procedures that support normal development of the oral structures. In general, frenuloplasty is a procedure that is performed in office settings to treat older children with ankyloglossia. It is considered a minimally invasive surgical procedure.
Frenuloplasty can be performed under local anesthesia, general anesthesia, or intravenous sedation. The procedure can be done in a clinic or at a hospital.
Postoperative care for patients with ankyloglossia includes routine evaluations, speech therapy, and follow-up for complications. For example, some children report social difficulties because they can’t stick out their tongue.
Surgical intervention for ankyloglossia is recommended when there are clear physical findings of the condition. It should be individualized to each child’s individual needs. Ideally, frenotomy should be performed before three months of age.
A two-year-old boy was referred to the Clinic of Pediatric Dentistry with ankyloglossia. His family history was not significant. Ankyloglossia was also diagnosed in an eight-year-old female patient. Her height and weight were appropriate for her age.
There are several surgical options available for infants with ankyloglossia. Frenuloplasty is a minor procedure that can be performed in the clinic, at the hospital, or at a children’s dentistry practice.
Laser therapy is another option for infants with ankyloglossia. This laser procedure can reduce the use of local anesthetics and reduce bleeding.
Post-procedure stretches
Post-procedure stretches after tongue tie are important to preventing wound reattachment and healing at a faster rate. To be successful, you need to perform the proper number of stretches. Stretches should be done at least six times a day. For optimal results, try to incorporate play into your daily routine. After surgery, you should also ask your doctor for recommendations on what medications to take.
The most important part of any post-procedure stretching regimen is making sure your hands are clean. This includes washing and wiping your fingers and your lips. In order to get the most out of your exercises, do not go overboard with your hand soap or alcohol. You should also use your thumbs to your advantage.
In addition to the above mentioned stretches, you should consider other post-surgery activities like feeding and playing. Do not neglect these tasks as they are essential to the well-being of your infant. Also, incorporating these tasks into your daily routine is a great way to bond with your child.
Hopefully, your child will be back to his or her old self in no time at all. However, it is not uncommon for the newfound freedom to disappear within the first 24 hours. Keeping your child in check will help minimize the likelihood of unwanted surprises. During this time, you may also want to make sure you are a good role model. If you are a parent, be sure to let your child know that you are proud of them and will do everything in your power to help them succeed.
Finally, don’t forget to keep a close eye on your kid’s diet. Getting enough protein and fiber is crucial to maintaining the health of your baby’s tongue. Likewise, be sure to consume plenty of water throughout the day.

Comments are closed.